CHEMISTRY
Paper 4 (P4): The Particulate Nature Of Matter Topic Quiz 1
Question 1:
Describe the separation, arrangement and motion of particles of an element in the solid state.
separation .............................................................................................................................................
arrangement ...........................................................................................................................................
motion ..................................................................................................................................................
[3]
[Total: 3]
Describe the separation, arrangement and motion of particles of an element in the solid state.
separation .............................................................................................................................................
arrangement ...........................................................................................................................................
motion ..................................................................................................................................................
[3]
[Total: 3]
Question 2:
Ammonia gas is prepared at the front of a laboratory.
The pungent smell of ammonia spreads throughout the laboratory slowly.
(a) Name the process that occurs when ammonia gas spreads throughout the laboratory.
.............................................................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) Explain, using ideas about particles, why ammonia gas spreads throughout the laboratory.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................................. [2]
(c) Explain why carbon dioxide gas, CO₂, will spread throughout the laboratory at a slower rate than ammonia gas, NH₃.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................................. [1]
[Total: 4]
Ammonia gas is prepared at the front of a laboratory.
The pungent smell of ammonia spreads throughout the laboratory slowly.
(a) Name the process that occurs when ammonia gas spreads throughout the laboratory.
.............................................................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) Explain, using ideas about particles, why ammonia gas spreads throughout the laboratory.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................................. [2]
(c) Explain why carbon dioxide gas, CO₂, will spread throughout the laboratory at a slower rate than ammonia gas, NH₃.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................................. [1]
[Total: 4]
Question 3:
The graph shows the change in temperature as a sample of a gas is cooled.
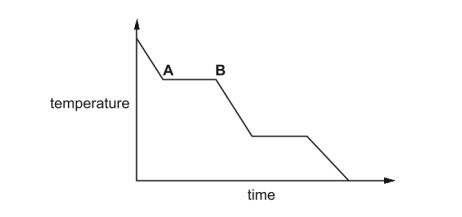
Name the change of state taking place between A and B.
..................................................................................................................... [1]
[Total: 1]
The graph shows the change in temperature as a sample of a gas is cooled.

Name the change of state taking place between A and B.
..................................................................................................................... [1]
[Total: 1]
Question 4:
Complete the table about solids, liquids and gases.
[Total: 3]
Complete the table about solids, liquids and gases.
| State | Particle Separation | Particle Arrangement | Type of Motion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | Regular | Vibrate only | |
| Liquid | Touching | Random | |
| Gas | Apart | Random |
[Total: 3]
Question 5:
A bottle of liquid perfume is left open at the front of a room.
After some time, the perfume is smelt at the back of the room.
Name the two physical processes taking place.
1.
2.
[2]
[Total: 2]
A bottle of liquid perfume is left open at the front of a room.
After some time, the perfume is smelt at the back of the room.
Name the two physical processes taking place.
1.
2.
[2]
[Total: 2]
Question 6:
Z is a covalent substance. In an experiment, a sample of pure solid Z was continually heated for 11 minutes.
The graph shows how the temperature of the sample of pure Z changed during the first 9 minutes.
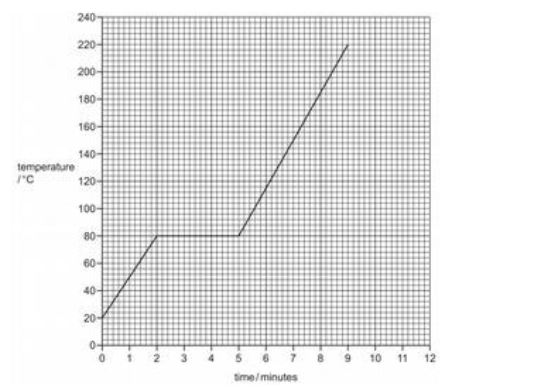
(a) What is the melting point of pure Z?
°C
(b) The sample of pure Z began to boil at 9 minutes. It was boiled for 2 minutes.
Use this information to sketch on the grid how the temperature of the sample of pure Z changed between 9 minutes and 11 minutes.
(Sketch space below)
(c) The sample of pure Z was continually heated between 2 minutes and 5 minutes.
Explain, in terms of attractive forces, why there was no increase in the temperature of the sample of pure Z between 2 minutes and 5 minutes.
(d) Describe how the motion of particles of pure Z changed from 0 minutes to 2 minutes.
[Total: 6]
Z is a covalent substance. In an experiment, a sample of pure solid Z was continually heated for 11 minutes.
The graph shows how the temperature of the sample of pure Z changed during the first 9 minutes.

(a) What is the melting point of pure Z?
°C
(b) The sample of pure Z began to boil at 9 minutes. It was boiled for 2 minutes.
Use this information to sketch on the grid how the temperature of the sample of pure Z changed between 9 minutes and 11 minutes.
(Sketch space below)
(c) The sample of pure Z was continually heated between 2 minutes and 5 minutes.
Explain, in terms of attractive forces, why there was no increase in the temperature of the sample of pure Z between 2 minutes and 5 minutes.
(d) Describe how the motion of particles of pure Z changed from 0 minutes to 2 minutes.
[Total: 6]
Question 7:
Z is a covalent substance. A sample of pure Z was allowed to cool from 120°C to 20°C. The total time taken was 8 minutes.
The boiling point of pure Z is 220°C and the melting point of pure Z is 80°C.
Starting from point x, sketch on the grid how the temperature of the sample of pure Z changed between 0 minutes and 8 minutes.
[Total: 1]
Z is a covalent substance. A sample of pure Z was allowed to cool from 120°C to 20°C. The total time taken was 8 minutes.
The boiling point of pure Z is 220°C and the melting point of pure Z is 80°C.
Starting from point x, sketch on the grid how the temperature of the sample of pure Z changed between 0 minutes and 8 minutes.

[Total: 1]
Question 9:
The image shows a cooling curve graph for a substance that starts as a gas at a high temperature (~300 °C) and cools over 30 minutes. The temperature changes are labeled with letters S to Z at various points and plateaus along the curve.
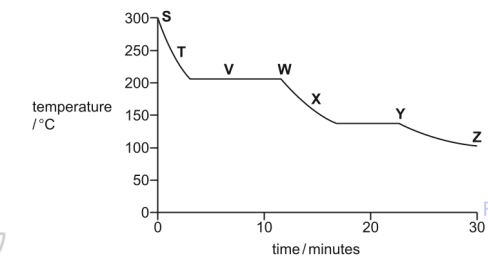
Each letter on the graph may be used once, more than once or not at all.
(a) Which letter, S, T, V, W, X, Y or Z, shows when
(i) the particles in the substance have the most kinetic energy:
(ii) the particles in the substance are furthest apart:
(iii) the substance exists as both a gas and a liquid:
(b) Use the graph to estimate the freezing point of the substance.
°C
[Total: 4]
The image shows a cooling curve graph for a substance that starts as a gas at a high temperature (~300 °C) and cools over 30 minutes. The temperature changes are labeled with letters S to Z at various points and plateaus along the curve.

Each letter on the graph may be used once, more than once or not at all.
(a) Which letter, S, T, V, W, X, Y or Z, shows when
(i) the particles in the substance have the most kinetic energy:
(ii) the particles in the substance are furthest apart:
(iii) the substance exists as both a gas and a liquid:
(b) Use the graph to estimate the freezing point of the substance.
°C
[Total: 4]
Question 10:
When smoke is viewed through a microscope, the smoke particles in the air appear to jump around.
(a) What term describes this movement of the smoke particles?
(b) Explain why the smoke particles move in this way.
[Total: 3]
When smoke is viewed through a microscope, the smoke particles in the air appear to jump around.
(a) What term describes this movement of the smoke particles?
(b) Explain why the smoke particles move in this way.
[Total: 3]
Question 11:
Dust particles in the air move around in a random way.
(a) What term describes the random movement of the dust particles?
(b) Identify the particles in the air which cause the random movement of the dust particles.
(c) Explain why the dust particles move in this way.
[Total: 5]
Dust particles in the air move around in a random way.
(a) What term describes the random movement of the dust particles?
(b) Identify the particles in the air which cause the random movement of the dust particles.
(c) Explain why the dust particles move in this way.
[Total: 5]
Question 12:
When chlorine gas, Cl2, is put into a gas jar, it spreads out to fill the gas jar.
When bromine gas, Br2, is put into a gas jar, it also spreads out to fill the gas jar.
The process takes longer for bromine gas than for chlorine gas.
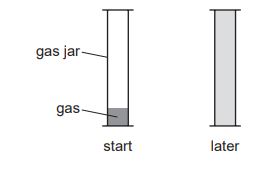
(a) What term describes the way that the gas particles spread out?
(b) Use data from the Periodic Table to explain why bromine gas takes longer to fill a gas jar than chlorine gas.
(c) Explain why increasing the temperature increases the rate at which the gas particles spread out.
[Total: 4]
When chlorine gas, Cl2, is put into a gas jar, it spreads out to fill the gas jar.
When bromine gas, Br2, is put into a gas jar, it also spreads out to fill the gas jar.
The process takes longer for bromine gas than for chlorine gas.

(a) What term describes the way that the gas particles spread out?
(b) Use data from the Periodic Table to explain why bromine gas takes longer to fill a gas jar than chlorine gas.
(c) Explain why increasing the temperature increases the rate at which the gas particles spread out.
[Total: 4]
Question 13:
Use ideas about the movement and arrangement of particles to explain why:
1. Solids have a definite volume and shape
2. Liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape
3. Gases have no definite volume or shape
[Total: 4]
Use ideas about the movement and arrangement of particles to explain why:
1. Solids have a definite volume and shape
2. Liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape
3. Gases have no definite volume or shape
[Total: 4]
Question 14:
Gallium and aluminium are in Group III of the Periodic Table.
The melting point of gallium is 30 °C.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain what happens when a spoon made of gallium is put into a cup of tea at 40 °C.
In your answer, refer to:
• the change of state which occurs,
• the change in the arrangement of the particles,
• the change in the motion of the particles.
[Total: 4]
Gallium and aluminium are in Group III of the Periodic Table.
The melting point of gallium is 30 °C.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain what happens when a spoon made of gallium is put into a cup of tea at 40 °C.
In your answer, refer to:
• the change of state which occurs,
• the change in the arrangement of the particles,
• the change in the motion of the particles.
[Total: 4]
Question 15:
A student placed a crystal of iodine in a test tube of solvent.
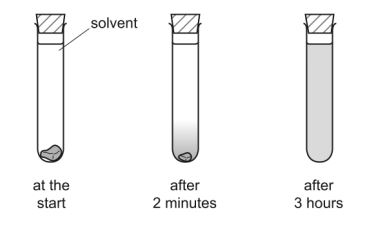
After two minutes, a dense violet colour was observed at the bottom of the test tube. After three hours, the violet colour had spread throughout the solvent.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain these observations.
In your answer, refer to:
• the arrangement and motion of the molecules in the iodine crystal,
• the arrangement and motion of the molecules in the solution,
• the names of the processes which are occurring.
[Total: 4]
A student placed a crystal of iodine in a test tube of solvent.

After two minutes, a dense violet colour was observed at the bottom of the test tube. After three hours, the violet colour had spread throughout the solvent.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain these observations.
In your answer, refer to:
• the arrangement and motion of the molecules in the iodine crystal,
• the arrangement and motion of the molecules in the solution,
• the names of the processes which are occurring.
[Total: 4]
Question 16:
A student took two identical syringes.
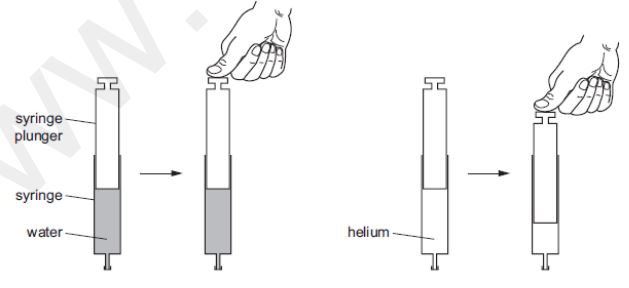
He filled one with water and the other with helium gas and sealed the end of both syringes. He then pushed the syringe plungers with equal force.
The diagram shows what happened.
Describe and explain these results using ideas about particles in liquids and gases.
[Total: 4]
A student took two identical syringes.

He filled one with water and the other with helium gas and sealed the end of both syringes. He then pushed the syringe plungers with equal force.
The diagram shows what happened.
Describe and explain these results using ideas about particles in liquids and gases.
[Total: 4]
Question 17:
The table shows some properties of the Group 0 elements helium, neon, argon and krypton.
Which element in the table has the highest melting point?
[Total: 1]
The table shows some properties of the Group 0 elements helium, neon, argon and krypton.
| Element | Electron Arrangement | Density of Liquefied Gas (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helium | 2 | 0.15 | -272 | -269 |
| Neon | 2,8 | 1.20 | -248 | -245 |
| Argon | 2,8,8 | 1.40 | -189 | -186 |
| Krypton | 2,8,18,8 | 2.15 | -157 | -152 |
Which element in the table has the highest melting point?
[Total: 1]
Question 18:
The table shows some properties of the Group 0 elements helium, neon, argon and krypton.
What is the state of argon at -188 °C?
[Total: 1]
The table shows some properties of the Group 0 elements helium, neon, argon and krypton.
| Element | Electron Arrangement | Density of Liquefied Gas (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helium | 2 | 0.15 | -272 | -269 |
| Neon | 2,8 | 1.20 | -248 | -245 |
| Argon | 2,8,8 | 1.40 | -189 | -186 |
| Krypton | 2,8,18,8 | 2.15 | -157 | -152 |
What is the state of argon at -188 °C?
[Total: 1]
Question 19:
A teacher placed some highly-scented flowers at the front of the class.
At first, the students at the back of the class could not smell the scent. After two minutes they could smell the scent.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain these observations.
[Total: 3]
A teacher placed some highly-scented flowers at the front of the class.
At first, the students at the back of the class could not smell the scent. After two minutes they could smell the scent.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain these observations.
[Total: 3]
Question 20:
Copper(II) sulfate is heated strongly. The products are copper(II) oxide and sulfur trioxide.
CuSO₄ → CuO + SO₃
The diagram below shows the arrangement of sulfur trioxide molecules at 30°C.
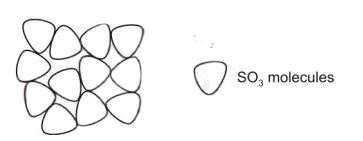
What is the state of sulfur trioxide at 30°C?
Use the information in the diagram to explain your answer.
[Total: 3]
Copper(II) sulfate is heated strongly. The products are copper(II) oxide and sulfur trioxide.
CuSO₄ → CuO + SO₃
The diagram below shows the arrangement of sulfur trioxide molecules at 30°C.

What is the state of sulfur trioxide at 30°C?
Use the information in the diagram to explain your answer.
[Total: 3]
Solution
Solution

